
Symmary of properties (F) Atomic weight 18.998403163(6) Discoverer (year) Moissan, Henri (1886) Natural form gas (F 2) Electron configuration 2 s 2 2 p 5 M.p. These spectra are usefull to identify the elements present in a sample. This results in a characteristic emission line in the spectra (which corresponds to specific wavelengths of light). When an electron in an atom is excited to a higher energy level, it can de-excite by emitting a photon of light with an energy equal to the difference between the two levels. The orbitals are filled in a specific order, starting with the lowest energy orbital and working up.Įach element in the periodic table presents its own unique emission spectra, which is determined by the energy levels of its electrons. In the electron configuration notation, the letters "s", "p", "d", and "f" represent the different types of atomic orbitals, and the superscripts indicate the number of electrons in each orbital. The electron configuration of an element describes the arrangement of electrons in the atoms of that element, and be used to predict its chemical properties and reactivity. One of the most common uses of fluorine compounds is as an additive in toothpaste, as it hardens teeth and prevents tooth decay. Also, PTFE fibers are used to make lightweight, waterproof clothing. Another derivative, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is commonly used to make nonstick pans. When heated, these glazes release fluorine, which hardens the ceramic.
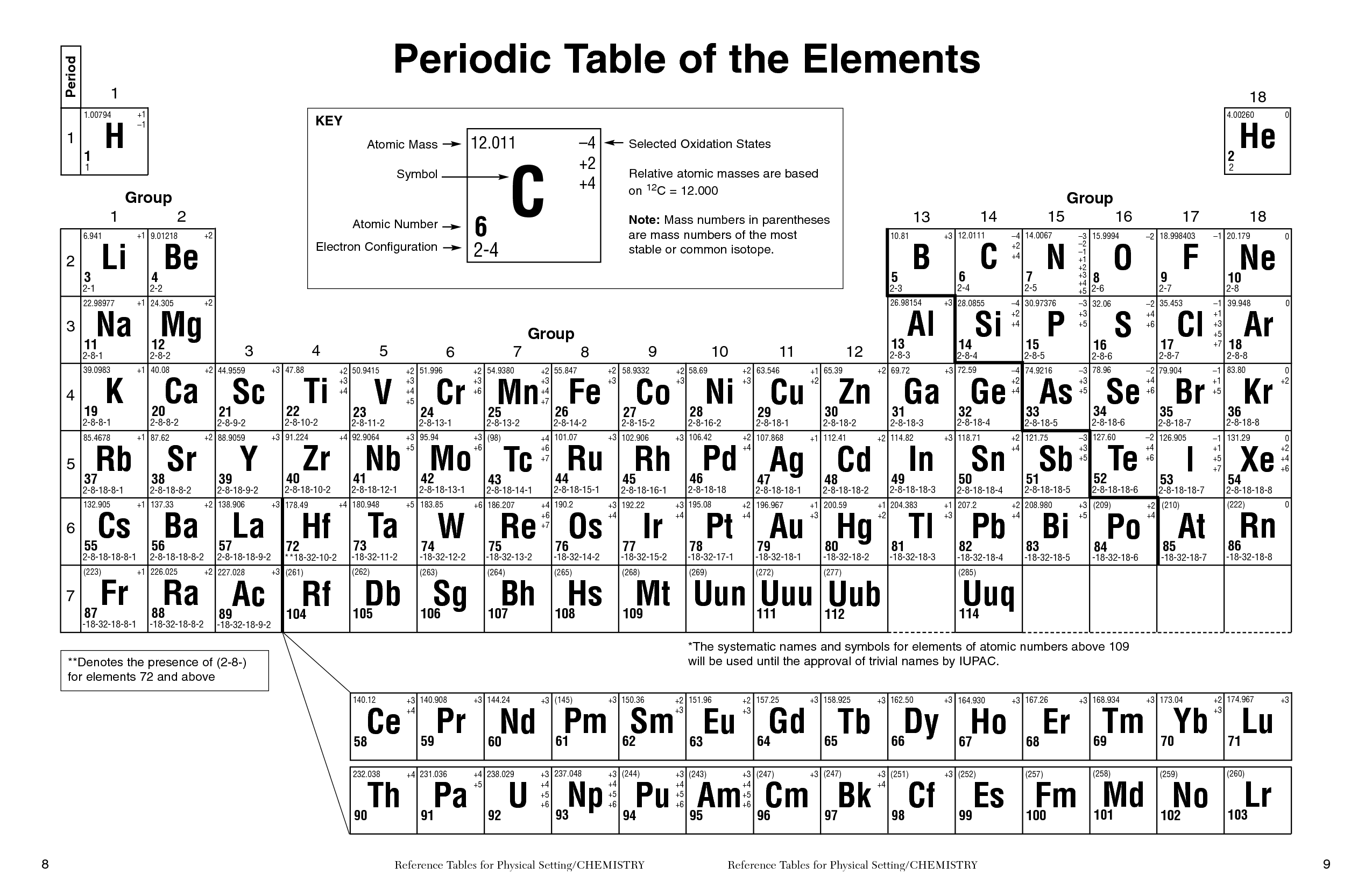
Some glazes used to coat ceramics contain fluorine minerals. Hydrofluoric acid, HF, is a toxic liquid used to etch patterns on glass. This gas and its less harmful compounds have a wide variety of uses, including in the production of fluorine-containing compounds such as hydrofluoric acid, and in the production of refrigerants and other chemicals. Minerals such as cryolite and fluorspar (fluorite) contain this element. Because it is so dangerous, in its pure state it is stored in containers made of nickel that can withstand its attack. It is highly reactive and forms compounds with almost all other elements. Moreover, it reacts with all kinds of materials, bricks, glass and steel, piercing them directly. Fluorine is the lightest halogen, and is the most powerful oxidizing agent known. It is the most reactive and electronegative element, and is a pale yellow, corrosive, and toxic gas at standard temperature and pressure. Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
